Describe How the Animal Hydra Reproduces Asexually by Budding
Hydra is considered to be an animal with low quality. The buds form from the body wall grow into miniature adults and break away when mature.
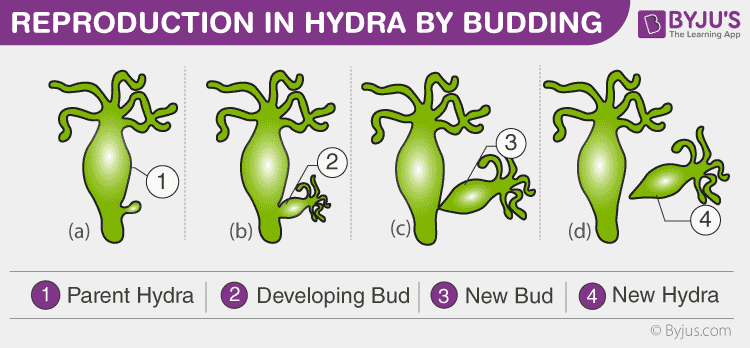
Budding An Overview Of Budding In Hydra And Yeast Cells
Then continuing the process of tentacle budding.

. These organism use regenerating cellsFirst a small outgrowth called bud is formed on the side of its body by division of its cellsThis bud then grows gradually to form a small hydraFinally the tiny new hydra. The process of budding in hydra is is a form of asexual reproduction. When conditions are harsh often before winter or in poor feeding conditions sexual reproduction occurs in some Hydra.
As a result a new organism is formed. These multicellular animals form a small bud which grows gradually. This is called budding.
For example the small bulb-like projection coming out from the yeast cell is known as a bud. When food is plentiful many hydras reproduce asexually by producing buds in the body wall which grow to be miniature adults and simply break away when they are mature. This is also one of the type of asexual reproduction.
Tentacles will form on the hydras body and eventually form a bud which will leave the mother cell when able to live on its own. A bud forms on the tubular body of an adult hydra develops a mouth and tentacles and then detaches from its parent. Yeast also reproduces by budding.
In regeneration the organisms have the. Organisms such as hydra use regenerative cells for reproduction in the process of budding. Asexual mode of reproduction can take place by several methods like Budding- Certain cells like yeast multiply by budding.
A small part of the body of parent organism grows out as a bud which then detaches and become a new organism. It is the type of asexual reproduction in which a small part of the body of the parent organism detaches and matures and becomes a new organism. Once grown the new organism detaches from the.
These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature detach from the parent body and become new independent individuals. Since the reproduction is asexual the newly created organism is a clone and is genetically identical to the parent organism. Describe your organism using words.
Budding is another method of asexual reproduction where a new organism develops from an outgrowth from the parent body known as a bud. When a hydra is well fed a new bud can form every two days. B Some coral such as the Lophelia pertusa shown here can reproduce through budding.
Describe both sexual and asexual reproduction in hydra. Asexual reproduction takes place either by budding or by fission. Figure 133 a Hydra reproduce asexually through budding.
During the budding the hydra develops a bud like structure on its body this is called bud. Hydras reproduce asexually by budding a process in which a bud breaks off an adult hydra and floats away. Animals like hydra reproduce through budding.
Budding is an asexual method of reproduction in animals. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction seen in Coelenterates eg. This bud then grows into an independent new organism.
A bud is usually formed in the middle of the body by rapid multiplication of interstitial cells. Gradually this bud grows and developed into a new individual and gets separated from the parents hydra. The stinging cells which.
This process of reproduction is referred to as asexual reproduction. Figure 133 a Hydra reproduce asexually through budding. In the animal kingdom reproduction is a necessary part of species survival.
During this process a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell divisions at one specific site. The hydra is a very small simple animal that lives in water. When conditions are harsh often before winter or in poor feeding conditions sexual reproduction occurs in some Hydra.
Since the reproduction is asexual the newly created organism is a clone and excepting mutations is genetically identical to the parent organism. Hydra can also reproduce sexually but most often reproduce asexually through budding. A bud forms on the tubular body of an adult hydra develops a mouth and tentacles and then detaches from its parent.
Budding appears to be the normal method of reproduction in Hydra and occurs at all times of the year. These buds develop into tiny individuals and when fully mature they get detached from the parent body and become new independent individuals. When conditions are harsh often before a cold winter sexual reproduction occurs in some hydras producing unfertilized eggs.
In hydra a bud develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site. Swellings in the body wall. The buds form from the body wall grow into miniature adults and break away when mature.
Learn about 12 animals that reproduce asexually and dont need a mate. Describe how hydra capture prey. Budding is a type of asexual reproduction in which a new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular site.
The bud grows slowly into a young animal and then detaches itself from the parent body. So the correct answer is Budding. The body of the animal starts developing a small bulging structure called bud which slowly grows and have itself disconnected from the parent animal and becomes a separate individual.
The daughter cell formed is generally smaller than the mother cell. When food is plentiful many Hydra reproduce asexually by budding. Hydra reproduce asexually by producing buds in the body wall which grow to be miniature adults and break away when they are mature.
It needs only a single parent to reproduce. B Some coral such as the Lophelia pertusa shown here can reproduce through budding. Sexual- Testes6-8 in number form from interstitial cells that produce a swelling in the upper third of the bodySpermatogenesis results in flagellated spermatozoa.
Hydra reproduces by asexual and sexual methods. When a hydra is well fed a new bud can form every two days. Hydra which is simple multicellular animal reproduces by budding.
These derive nutrition from the parent for growth and development. When food is plentiful many Hydra reproduce asexually by budding. The asexual reproduction by budding is observed in hydra and yeast.
The new hydra is fully developed and will find its own location for attachment. It results in the mother cell and a daughter cell. The new hydra is fully developed and will find its own location for attachment.
Certain multicellular organisms like hydra reproduce by bud formation.

Hydra Reproduction Budding And Sexual Regeneration Immortality

Hydra Reproduction Budding And Sexual Regeneration Immortality
Asexual Reproduction In Animals Learn Biology Class 8 Amrita Vidyalayam Elearning Network
0 Response to "Describe How the Animal Hydra Reproduces Asexually by Budding"
Post a Comment